Apart from trading Forex, stocks and bonds, options trading is another way to invest in securities.
Although some traders tend to confuse Forex trading and options trading, these are far different things.
In options, Trades expire after a specific time while in Forex trading, you dictate when to close a trade.
To do options trading, you first have to know what they are. In this lesson we shall mainly concentrate on what options are and how they work.
What is Options Trading?
Options are financial derivative contracts between the buyer and the seller.
The buyer has the right but not an obligation to buy a security or other financial asset at a specified price within a specified period of time.
On the other hand, the seller has the obligation to carry out the transaction if the buyer chooses to exercise it.
In other words, it’s optional for the buyer to buy, not an obligation.
If the buyer is no longer interested in the contract, he/she can let go. Or else, he/she can choose to go on with the contract only if it will benefit.
However, it is an obligation for the seller to carry out the transaction as long as the buyer chooses to exercise it.
Example on Options Trading
In case your friend is selling a nice car but you don’t have enough money to pay for it.
Then you negotiate and he agrees to sell it to you. But only if you make a deposit and complete payment in a months’ time.
Suppose the cost of the car is $50,000.
If he requires a deposit of $5000, the remaining balance is $45000. You must pay this at the end of the month according to the contract.
Fortunately, in the course of the month you land on your dream car being sold at the same exact amount as that of your friends car.
Now you have two options.
You can choose to purchase your dream car not your friends car because it’s not an obligation that you must buy it.
Or, choose to go on and buy your friends car.
Never the less, if you don’t buy the first car, you will have to lose the money you paid as deposit for booking.
For the seller (your friend), after the agreement that you will finish payment in a months and someone else offers a higher price for the car, it’s not your problem.
You will still pay the same amount as agreed upon in the contract because you have the right. The seller has no right to sell to another person as long as he is already in agreement.
How does Option trading works
You can buy or sell options on the options market.
However, options are not the same thing as stocks because they do not get ownership in a company.
When buying or selling options, the trader has the right to exercise that option at any point up until the expiration date.
The price at which you agree to buy the underlying security on the option market is the strike price.
Conversely,the fee you pay for buying that option contract is the premium.
When determining the strike price, you are betting that the underlying security will go up or down in price.
The underlying security is one in which an option derives value from. These include ;
- Stocks
- Bonds
- Indices
- Foreign currencies
- other financial assets.
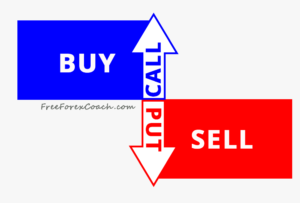
There are 2 different kinds of options; Call and Put options.
Call Options
A call option contract gives the owner the right to buy a specified security at a specified price within a specified time frame.
If you’re buying a call option, it means you want the stock (or other security) to go up in price so that you can make a profit. You later sell them back on the profit.
The cost of buying the contract is the premium.
Put Options
A put option however is a contract that gives a trader the right to sell a certain security at a specified price in a a specified time.
Just like call options, a put option allows the trader the right (but not obligation) to sell a security by the contract’s expiration date.
Unlike a call options, for a put option you want the security to drop in price to make a profit.
Common terms used in options trading.
Premium
The payment for buying or selling an option.
Strike price/ exercise price.
The pre-decided price at which the asset can be bought or sold.
Expiration date.
The future date on or before which the option contract can be executed. Time at which a trade is closed or settled.
Lot size
The fixed number of units of the underlying stock that form a single future or option contract.
Open interest
Total number of the outstanding positions on a particular options contract across all participants in the market at any given time.
Common mistakes most traders make and how to avoid them?
Fear and greed are the number one causes for the common mistakes most traders make when trading. Fear and greed normally come before trading, during and after trading. When you are under fear or greed, you are likely to commit these mistakes most traders make; Get...
- Oh, bother! No topics were found here.